NTA NET GEOGRAPHY PYQS- MODELS AND THEORIES, 2020-2006, PART-2
1. Who amongst the following propounded the ‘Theory
of Intervening Opportunities’?
a. E.G Ravenstein
b. G.K.Zipf
c. D.J Bogue
d.
S. Stouffer
2. Which one of the following is not matched
correctly?
|
a |
M.T. Sadler |
Economic Theories of
Population Growth |
|
b |
W.C.
Plowden |
Census
of India |
|
c |
F.W.
Notestein |
Demographic
Transition |
|
d |
E.G.
Ravenstein |
Laws
of Migration |
3. As per Edward Ullman’s mode of transport system,
which one of the following describes complementarity?
1. Demand and supply of a
product between regions
2. Cost of movement of a product between regions
3. Availability of a product in a region
4. Non-availability of a product in a region
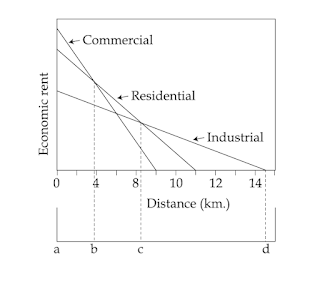
4. Which one of the following categories of urban
land use as per given graph has the highest gradient of its economic rent at 2
km distance?
1. Green land
2. Residential
3. Industrial
4.
Commercial
5. Which one
of the following authors initiated concept of ‘Isodapanes’ in space-economy?
a. A. Losch
b. A. Weber
c. E. Hoover
d. T. Planer
5. Which one of the following indices is used to
indicate if the optimal location was closer to either raw material source or
the market?
a.
Material Index
b. Labour Cost Index
c Relative Spread Index
d. Weighted Index
6. Which one of the following principles is
representative of the following figure of Christaller's Model?
1. Transport Principle
2.
Administrative Principle
3. Marketing Principle
4. Threshold Principle
7. Which one of the following economic principles is
correct for organisation of settlements based on K= 4 presented in the
Christaller's central place model?
1. Agricultural activities
2. Transport
3. Administrative
4. Marketing
8. The Two Cycle Theory on the origin of limestone
caverns was proposed by
1.
Davis
2. Gardner
3. Malott
4. Swinerton
9. Which one of the following statements correctly
explains the difference between Gravity model and Potential model?
a.
Gravity model deals with only two places at a time, while Potential model
accounts for interactions between many places.
b. Gravity model makes no provision for size of
places, while Potential model considers size of places.
c. Both Gravity model and Potential model are the
same.
d. Gravity model does not take distances into
account, while Potential model takes distances into account.
10. Given below are two statements, one is labelled
as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements
and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
Assertion (A): Central Business District (CBD) of a
city has high concentration of wholesale stores, offices and cultural and
recreational activities.
Reason (R): Prices and demand of real estate
increases as distance towards CBD reduces.
Code:
a. (A) is true, but (R) is false.
b. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the
correct explanation of (A)
c.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
d. (A) is false, but (R) is true.
11. Match List I with List II and choose the correct
answer from the code given below
|
List
I (Model Concept) |
List
II (Definition) |
|
(a)
Sector Model |
(i)
Model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are
spatially arranged in a series of rings |
|
(b)
Concentric Zone Model |
(ii)
Nucleus of a city where retail stores and offices are concentrated |
|
(c)
Bid-Rent theory |
(iii)
Theory that refers how price and demand on real estate changes as
distance towards CBD increases. |
|
(d)
Central Business District (CBD) |
(iv)
Model of internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged
around a series of sectors or wedges radiating from CBD |
Code:
1. (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
2. (a)-(iv), (b)-(i), (c)-(iii),
(d)-(ii)
3. (a)-(iii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(ii)
4. (a)-(i),
(b)-(i), (c)-iv), (d)-(iii)
12. Which one of the following statements correctly
depicts the threshold according to Central Place Model?
(a) Point at which consumer movement is minimum
(b) Distance far which consumer will travel for a
service
(c)
Minimum number of people needed to support a service
(d) Economic base of a centre
13.. Which one of the following Models is explained
by the given figure below?
(a) Weber’s Model
(b)
Central Place Model
(c) Von Thunen Model
(d) Gravity Model
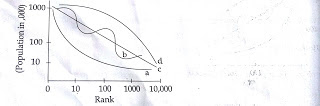
14. Which one of the following code is correctly
depicting the pattern of distribution of population among cities by ‘d’ curve
in the given graph?
Code:
(a) Primate
(b) Stepped order
(c)
Binary
(d) Rank Size Rule
15. Which one of the following statements indicates
to the potential use of a service at a location according to Gravity Model?
(a) Direct relationship to both population size and
distance
(b) Inverse relationship to both population size and
distance
(c)
Direct relationship to both population size and inverse relationship to
distance
(d) Direct relationship to distance and inverse
relationship to population
16.. Among the following scholars, who introduced
the concept of ‘Least-Transport-Cost Location’ using the frame of ‘Location
triangle’?
a) W.Isard
b) M.K Bandman
c) D.M. Smith
d)
A. Weber
17. Which one of the following conditions Alfred
Weber introduced in his concept of ‘Locational Triangle’?
a) Both ‘R1’ and ‘R2’ are found universally
b) ‘R1’ is fixed but ‘R2’ is found everywhere and
both are pure
c) Both ‘R1’ and R2 are fixed and pure
d)
Both ‘R1’ and ‘R2’ are fixed and gross
18. The Rimmer model for the development of land
transport system in less developed economics was proposed in which of the
following years?
(1) 1975
(2) 1976
(3)
1977
(4) 1978
19.. Which one of the following statements is very
correct in context of the concept of Growth pole and growth centres?
(a) Both the Growth pole and Growth centres are
uniformly distanced in the region.
(b) Lower order Growth centers are located quite far
away as compared to higher order Growth centres.
(c)
Higher order Growth centres are located far away while lower order Growth
centres are located closer to one and another.
(d) There does not exist any rule in the distance
between Growth pole and Growth centres.
20. Which one of the following principles denotes
K-4 of Christaller’s Model of central places?
(a) Market
(b) Administrative
(c)
Transport
(d) Economic
21. Which one of the following was not assured by
weber in his least-cost theory?
(a)
Agglomeration economies lead to high transport and labour cost
(b) Labour is infinitely available
(c) Location with high transport costs may be
attractive because of a cheap labour supply
(d) Transport costs were uniform by distance and
weight in any direction
22. Which one of the following is not included in
the Ravenstein’s Laws of migration?
(a) Most migrants proceeds step by step
(b) Most migrants go for short distance
(c)
Most migrants move from Urban to Rural area
(d) Most migrant are adults
23. Which ONE of the following is not in conformity
with the central place theory?
(1) Central place is a settlement providing services
for the population of its hinterland.
(2) Hierarchy and nesting pattern results in maximum
number of central places
(3)
Ubiquities and localized raw materials
(4) Market areas for different goods resemble nets
of hexagons
24. Match List-I with List–II and select the correct
answer from the codes given below:
|
List-I
(Terms) |
List-II
(Description) |
|
I.
Material index |
A.
ratio of the labour cost per unit of product to the locational weight of that
unit |
|
II.
Isodapanes |
B.
Advantage of production due to the concentration of industry |
|
III.
Labour Co-efficient |
C.
Weight of localized material and the weight of the product |
|
IV.
Agglomeration |
D.
Lines of equal transport costs per tonne |
Codes:
|
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
|
1 |
C |
D |
A |
B |
|
2 |
D |
C |
B |
A |
|
3 |
D |
B |
C |
A |
|
4 |
B |
D |
A |
C |
25. The gravity principle in identification of nodal
regions states that the interaction between two geographical points is directly
related to their
(1) Distance
(2)
Masses
(3) Size of settlement
(4) Mode of transport
26. Which one of the following letters represent the
total number of settlements of a certain order served by a central place of the
next higher order?
A.
K
B. J
C. L
D. F
27. The rule “size of population of nth ranking town
in a region will be 1/nth of the largest city in terms of population’’ was
given by:
1. Mark Jefferson
2. J. Gattman
3.
G. K Zipf
4. C. D Harris and E. L Ullman
28. Who among the following is credited with
incorporation of concept of geographical space in the Growth Pole Theory?
A. Myrdal
B. Haggerstrand
C.
Boudeville
D. Friedman
29. Match List-I with List–II and select the correct
answer from the codes given below:
|
List-I
(Geographers) |
List-II
(Theories/Model/Concepts) |
|
I.
J. Gottmen |
A.
Concentric zone theory |
|
II.
E. Burgess |
B.
Primate city |
|
III.
M. Jefferson |
C.
Multiple Nuclei model |
|
IV.
C. Harris and E. Ullman |
D.
Megalopolis |
Codes:
|
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
|
1. |
A |
D |
C |
B |
|
2. |
B |
A |
D |
C |
|
3. |
C |
B |
A |
D |
|
4. |
D |
A |
B |
C |
30. What are the three basic aspects for spatial
interaction are as described in Edward Ullman’s model?
A. Human behaviour, Transferability, Convenience
B. Surplus-deficit relationship, Commuity specific
relationship, Complementarity
C.
Complementarity, Intervening Opportunity, Transferability
D. Residential neighbourhood, Complementarity,
Convenience
31.. Given below are two statements, one labelled as
Assertion (A) and other labelled as Reason (R). Select your answer from the
codes given below: (Q.17.)
Assertion (A): Losch’s model is less restrictive
than Christallers’s model
Reason (R): Losch treated each section as having
separate range, threshold and hexagonal hinterland.
Codes:
(1)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(2) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the
correct explanation of (A).
(3) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(4) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
32. Which one of the following principles explains
importance of transport costs as it maximises the number of central places on
straight line routes?
(1) Traffic
(2) Administrative
(3) Marketing
(4) Service
33. Which one of the following contributors made
refinements to W. Christaller’s central place by including concept of ‘city
rich’ sectors and ‘city poor’ sectors?
(A) R.P. Mishra
(B) B.J.L. Berry
(C) Walter Isard
(D)
August Losch
34. In which year, M. Jefferson examined the size
relationship between the primate city and next largest cities in a study
entitled ‘The Law of the Primate City’?
(A) 1938
(B) 1937
(C) 1936
(D)
1939
35. Which one of the following authors identified
three basic factors affecting interaction between regions: Complementarily,
intervening opportunity and transferability?
(A) P.R. White
(B) H.L. Gauthier
(C) E. Taafe
(D)
Ullman
36. Which one of the following codes is correct to
show the optimal location to profitability in different spatial cost / revenue
situations in diagram given below?
Codes:
(1) A
(2)
B
(3) C
(4) D
37. The concept of liner market price boundary
between the market area of two competing firms was given by
(1) A. Weber
(2)
T. Palander
(3) E. Hoover
(4) A. Losch
38. Which one of the following authors suggested a
fivefold division of adopters on the basis of the time lag between receiving
and acting upon new information as shown in diagram below?
(1)
E.M. Rogers
(2) L.W. Bowden
(3) Z. Giriliches
(4) T. Hagerstrend
39. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct
answer from the codes given below:
|
List-I |
List-II |
|
(a)
Central Place Theory |
(i)
Land use pattern in large cities developed around a number of discrete
centres rather than a single centre |
|
(b)
Multiple Nuclei Theory |
(ii)
Position of the breaking point between two towns |
|
(c)
The Law of Retail Trade Gravitation
|
(iii)
Hexagonal Service Area |
|
(d)
Breaking Point Theory |
(iv)
Residential belt of considerable density surrounding the C.B.D |
Codes:
|
(a) (b) (c) (d) |
|
(1) (i) (iv)
(iii) (ii) |
|
(2) (iii) (i) (ii) (iv) |
|
(3) (iii)
(i) (iv)
(ii) |
|
(4) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i) |
40. Match List – I with List – II and select the
correct answer from the codes given below:
|
List
– I (Geographer) |
List-
II (Theory/Model) |
|
(a)
Philbrick |
(i)
Industrial Location |
|
(b)
Christaller |
(ii)
Economic Landscape |
|
(c)
Losch |
(iii)
Central Place |
|
(d)
Smith |
(iv)
Areal functional organization |
Codes:
|
(a)
(b) (c) (d) (1) (i) (ii)
(iii) (iv) (2) (iv) (iii)
(i) (ii) (3) (iv) (iii) (ii)
(i) (4) (i) (ii)
(iv) (iii) |
GEOGRAPHIA
If you want to join my telegram group
YOU TUBE CHANNEL LET'S LEARN GEOGRAPHY click here
NCERT CLASS_6 SHORT NOTE CLICK HERE
NCERT CLASS _6 SOLUTION CLICK HERE
ICSE class -ix click here
ICSE class -x click here
CLASS 6 WBBSE GEOGRAPHY CLICK HERE
জলবায়ুর শ্রেণীবিভাগপ্রশ্ন-উত্তর click here
REGIONAL THEORIES CLICK HERE
দ্বাদশ শ্রেণী ভূগোল CLICK HERE
CURRENT AFFAIRS CLICK HERE
NOTES OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY AND AND POPULATION GEOGRAPHY click here
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY FB TAYLOR CLICK HERE
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY TAYLOR IN BENGALI CLICK HERE
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY WEGNER CLICK HERE
CLIMATE OF INDIA CLICK HERE
ভূমিরূপ গঠন কারী প্রক্রিয়া ; উচ্চমাধ্যমিক ভূগোল click here
বহির্জাত প্রক্রিয়া ও তার ফলে সৃষ্ট ভূমিরূপ click here
মহিসঞ্চারন তত্ত্ব click here
Ugc net 2007 june paper 2 geography click here
Ugc net 2006 december paper 2 geography click here
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2007 DECEMBER CLICK HERE
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2008 JUNE CLICK HERE
WB CLASS 6 GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 4 CLICK HERE
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2009 JUNE CLICK HERE
PLATE TECTONIC THEORY CLICK HERE
NCERT CLASS 7 GEOGRAPHY CLICK HERE
CORAL REEF IN BENGALI NOTE CLICK HERE
CORAL REEF CLICK HERE
HS GEOGRAPHY CLICK HERE
geographical terms click here
NTA NET GEOGRAPHY PYQS- MODELS AND THEORIES, 2020-2006, PART-1 CLICK HERE
Thank you for visiting this page.we provide geography related study materials on daily basis..






.png)



0 Comments