CORAL REEF: LOCATION,THEIR MAJOR TYPE
Introduction
Coral reef and atolls are significant submarine features.
These are formed due to deposition and accumulation of skeletons of lime secreting
organisms known as coral polyps. It is basically a type of calcareous rock which
is made of skeletons of minute sea organisms known as polyps.
Features
1.
These small organisms exact calcium from the sea
water to build their skeleton for protecting their bodies.
2.
There are 1,000,000 species of coral polyps which
only 10% have been studied.
3.
They have a tendency to live in colonies
4.
Coral reefs are formed due to formation of one shell
upon another along submarine platforms at suitable depth.
5.
Coral reefs are more diverse than the tropical rain
forests
CONDITION FOR THE GROWH OF CORAL POLYPS
Coral animals need certain condition of temperature
, depth of water ,nature of seawater for their smooth survival and growth as
follows:
1. Location: coral polyps thrive in the tropical
oceans confined 30N -30S.
2. Temperature: coral polyps are temperature
sensitive shallow sea animals because they can neither very high temperature
nor very low temperature. 20c to 30c requires for the growth of polyps. Suitable
conditions are found in the tropical zone. more than 50 genera of coral polyps
found in the tropical pacific ocean and Indian ocean
3. Depth of seawater: sufficient sunlight requires
for the growth of coral polyps. Sunlight decreases with increasing the depth of
seawater. 45-55 meters suitable for the growth of coral polyps. Sunlight does
not favor coral animals directly.
4. Turbidity of Seawater: turbidity means cloudiness
of water caused by presence of suspended materials of inorganic origin. So it
is the density of suspended materials which determines the degree of turbidity
of seawater. Higher density of suspended materials and greater turbidity of
seawater. Coral polyps require clean sediment free water as the muddy water
clogs their mouth and they die.
5. Flux of
Fresh water: coral polyps avoid delta
regions, coastal regions because it requires sediment free water but fresh
water is also injurious for the growth of coral animals.
6.Ocean salinity: very high proportion of salinity
is injurious for the growth of coral polyps. because such water contains little
amount of calcium carbonates where lime is the main food of coral polyps. the
ocean salinity is ranging between 27 to 30 is ideal for the growth and
development of coral polyps.
7. ocean currents and waves: ocean currents and sea
waves are favourable for coral polyps because they provide necessary food .
8.submarine platform.: There should be extensive plateform for the formation of colonies of coral polyps. it should not be more than 50 fathoms(1 fathom= 6ft/1.8m)
CORAL ECOLOGY AND CORAL TYPES
The coral ecology means interactions between coral
animals and physical environment. There are different types of coral in
different environment.
(1) Hermatype coral
(2) Ahermatype coral
|
Hermatype
coral |
Ahermatype
coral |
|
They live in
group and build their colonies |
They live in
isolation as they are solitary by habit. |
|
They are
found in the tropical regions |
They are
found in throughout the world |
|
They don’t find
exceed 80 meters |
They can find shallow to deep water |
DISTRIBUTION OF CORAL REEFS
Corals are found in certain patches in the tropical region. Basically the coral reefs are abundantly found in the tropical Indo –
Pacific Oceans between 30S -20N.
55% of world corals are found in th western pacific
ocean and 30% of the coral are found in the Indian ocean.
INDIAN OCEAN:
East coast of Kenya, around Madagascar, south Africa
,western Australia, red sea , Maldives , Lakshadweep, Andaman and niccobar
PACIFIC OCEAN: Philippines, off southern coast of Japan,
Polynesia, Micronesia, Queensland of Australia
ATLANTIC OCEAN: Caribbean Sea, east coast of Brazil etc.
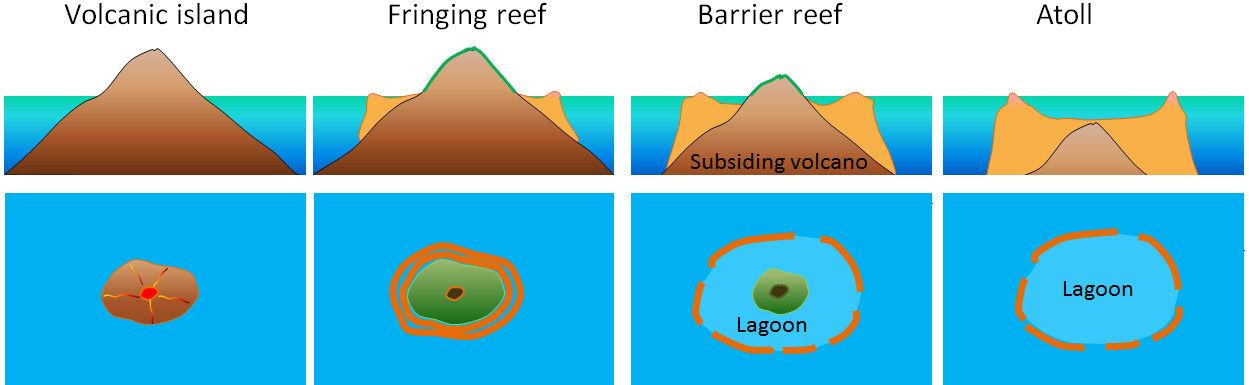
TYPE OF CORAL REEFS
The coral reefs are classified in two ways as
follows:
1. On the basis of geology , nature , shape and mode
of occurrences which is recognized by Charles Darwin during his study of coral
reef in pacific ocean
(a) FRINGING REEF
(b) BARRIER REEF
(c) ATOLL
2. On the basis of location
(a) Tropical coral reefs in extensive belts
(b) Marginal belts of coral reefs.
FRINGING REEF
1.
Coral reef developed along the continental margins
or along the islands is called fringing reef.
2.
The seaward slope is steep and vertical while
landward slope is gentle
3.
The upper surface is uneven and corrugated.
4.
It attaches to the coastal land but sometimes there
is gap between them and land.
5.
A lagoon is formed between land and reef such lagoon
is called boat channel.
6.
It is generally long but narrow in width.
Example: Sakau Island, Southern Florida, Methetia
etc.
BARRIER REEF:
1.
The largest coral reefs off the coastal platforms
but parallel to them are called barrier reef.
2.
They are the largest, most extensive, highest and
widest reef.
3.
the average slope of the reef is 45 degree but some
barrier reefs are characterized by 15 degree -25 degree
4.
There is extensive but shallow lagoon between
coastal land and barrier reef.
5.
Barrier reefs are seldom found as continuous chains
rather they are broken at many places thus the lagoon have contact with open
sea through tidal inlets.
Example: Great Barrier Reef, located parallel to the
east coast of Australia.
ATOLL
1.
A ring narrow growing corals of horse shoe shaped
and crowned with palm trees is called atoll
2.
It is generally found around an island or in
elliptical form on a submarine platform
3.
There is a lagoon in the middle of coral reef.
4.
The depth of the lagoon ranges between 40 to 70
fathoms.
Atolls are divided into three types
1. True atoll which are circular reef enclosing a
shallow lagoon without island
2. Island atoll having an island in the central part
of the lagoon enclosed by circular reef .
3. Coral island doesn’t have in the beginning but
later in island is formed due to erosion and deposition by marine waves.
Example: Antilles sea, red sea , china sea, Australian
sea , Indonesian sea etc.
SAYANTANI SINGH Msc, B.Ed
GEOGRAPHIA
Thank you for visiting this page.we provide
geography related study materials on daily basis..
If you want to join my telegram group
YOU TUBE CHANNEL LET'S LEARN GEOGRAPHY click here
NCERT CLASS_6 SHORT NOTE CLICK HERE
NCERT CLASS _6 SOLUTION CLICK HERE
ICSE class -ix click here
ICSE class -x click here
CLASS 6 WBBSE GEOGRAPHY CLICK HERE
জলবায়ুর শ্রেণীবিভাগপ্রশ্ন-উত্তর click here
REGIONAL THEORIES CLICK HERE
দ্বাদশ শ্রেণী ভূগোল CLICK HERE
CURRENT AFFAIRS CLICK HERE
NOTES OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY AND AND POPULATION GEOGRAPHY click here
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY FB TAYLOR CLICK HERE
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY TAYLOR IN BENGALI CLICK HERE
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY BY WEGNER CLICK HERE
CLIMATE OF INDIA CLICK HERE
ভূমিরূপ গঠন কারী প্রক্রিয়া ; উচ্চমাধ্যমিক ভূগোল click here
বহির্জাত প্রক্রিয়া ও তার ফলে সৃষ্ট ভূমিরূপ click here
মহিসঞ্চারন তত্ত্ব click here
Ugc net 2007 june paper 2 geography click here
Ugc net 2006 december paper 2 geography click here
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2007 DECEMBER CLICK HERE
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2008 JUNE CLICK HERE
WB CLASS 6 GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER 4 CLICK HERE
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY 2009 JUNE CLICK HERE
PLATE TECTONIC THEORY CLICK HERE
















0 Comments