Teacher-controlled instruction//RRB //TGT/PGT TEACHER
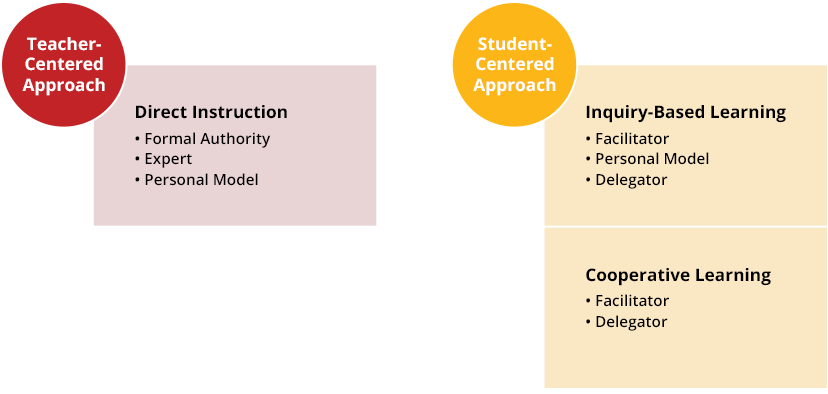
Teacher-controlled instruction is a teaching method where the teacher is the primary source of knowledge and instruction. The teacher plans and carries out the instruction, and decides what activities the students will do.
In a teacher-centered learning environment, the teacher functions in the familiar role of classroom lecturer, presenting information to the students, who are expected to passively receive the knowledge being presented.
Key features
The teacher is the main source of knowledge
The teacher plans and carries out the instruction
The teacher decides what activities the students will do
The teacher uses direct instruction, which is a passive learning strategy
Discipline Comparison in Teacher–Centered and Person–Centered Classrooms
Teacher–Centered ➖➖➖Person–Centered
👉Teacher is the sole leader➖➖➖ Leadership is shared
👉Management is a form of oversight➖➖➖ Management is a form of guidance
👉Teacher takes responsibility for all the paperwork and organization➖➖
👉Students are facilitators for the operations of the classroom
👉Discipline comes from the teacher➖➖➖ Discipline comes from the self
👉A few students are the teacher’s helpers➖➖➖ All students have the opportunity to become an integral part of the management of the classroom
👉Teacher makes the rules and posts them for all students ➖➖➖Rules are developed by the teacher and students in the form of a constitution or compact
👉Consequences are fixed for all students➖➖➖ Consequences reflect individual differences
👉Rewards are mostly extrinsic➖➖➖ Rewards are mostly intrinsic
👉Students are allowed limited responsibilities ➖➖➖Students share in classroom responsibilities
👉Few members of the community enter the classroom➖➖➖ Partnerships are formed with business and community groups to enrich and broaden the learning opportunities for students
Key Features:
👉Teacher as the Primary Authority:
The teacher is the central figure, responsible for planning, delivering, and evaluating the curriculum.
👉Teacher-Directed Instruction:
The teacher selects the topics, methods of instruction, and activities, with students primarily listening and following instructions.
👉Emphasis on Content Knowledge:
The focus is on transmitting information and knowledge from the teacher to the students.
👉Structured Learning Environment:
The classroom is organized and structured, with clear rules, routines, and expectations.
👉Independent Work:
Students often work individually on assigned tasks, with the teacher monitoring and correcting their work.
👉Limited Student Interaction:
Opportunities for student-to-student interaction and collaboration are limited.
👉Teacher-Led Discussions:
Discussions are typically initiated and led by the teacher, with students responding to questions and providing answers.
👉Focus on Standardized Assessment:
Assessments often take the form of standardized tests and quizzes, designed to measure student knowledge and understanding.
👉Clear Expectations and Routines:
Teachers establish clear expectations for student behavior and develop routines to maintain order and efficiency.
👉Emphasis on Compliance and Accuracy:
Students are expected to follow instructions, complete assignments accurately, and demonstrate mastery of the material.
Teacher-Centered Approach:
- The teacher is the primary source of information and knowledge.
- The teacher controls the learning environment and pace.
- Learning primarily takes place in a physical classroom setting.
Common Methods:
✔Lectures: The teacher delivers information to the students in a structured, one-way format.
✔Textbook-Centric Learning: A strong emphasis is placed on textbooks as the primary source of knowledge.
✔Worksheets: Students complete worksheets based on the material covered in lectures or textbooks.
✔Rote Memorization: Encouraging students to memorize facts and figures without necessarily understanding the underlying concepts.
✔Assessment: Traditional methods often rely on traditional tests and exams to assess student learning.
Advantages:
- Structured Learning: Traditional methods provide a structured and organized learning environment.
- Facilitates Large Group Instruction: Teacher-centered methods can be effective for conveying information to large groups of students efficiently.
- Easily measurable outcomes: The assessment methods can be quickly marked and graded.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Engagement: Students may find the traditional lecture format passive and unengaging.
- Limited Student Interaction: Students have limited opportunities for interaction with the teacher and other students.
- Focus on Knowledge Recall: Emphasis on memorization can hinder the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Does not account for diverse learning styles
1. CURRICULUM : 👉 CLICK HERE
2.INCLUSIVE EDUCATION 👉 CLICK HERE
3.GROSS MOTOR AND FINE MOTOR DEVELOPMENT 👉 CLICK HERE
4. GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT 👉 CLICK HERE
5. CTET SYLLBUS 👉 CLICK HERE
6. RRB TGT UNIT 1 PHILOSOPHICAL EDUCATION👉 CLICK HERE
7. CDP 30 QUESTION SERIES PART 1 👉 CLICK HERE
8. CDP 30 QUESTION SERIES PART 2 👉 CLICK HERE
10. SST 2023 AUGUST PAPER👉 CLICK HERE

.jpg)










0 Comments