CBSE CLASS 10 SST GEOGRAPHY AGRICULTURE // IMPORTANT QUESTION ANSWER
1.what are the main features of kharif crops and rabi crops.
answer:The three main features of Rabi crop are:
1. Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June.
2. Wheat, barley, peas, grams, and mustard are examples of Rabi crop.
3. During the winter months, the precipitation from western cyclone helps in the success of these crops.
The three main features of Kharif crop are:
1. Rabi crops are grown with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September- October.
2. Paddy, jowar, maize, and bajra are examples of Rabi crop.
3. These crops receive rain from southwest monsoon winds.
2,what is commercial farming?
answer:commercial crop farming is also known as agribusiness. It is a type of farming in which crops and livestock are raised to sell the products on the market for profit. Commercial farms are large farms and require huge capital investment.
3.what term describe the system where a single crops is grown on a large scale area.
answer: Plantation agriculture
4.what are reason of low juteproductionin india?
answer:Due to its high cost, jute is losing its market to synthetic fibres like nylon, resulting in its low production.
5.Irrigation has changed the cropping pattern of India?
answer:rrigation has changed the cropping pattern of many regions, due to the construction of dams in the following ways : (i) The farmers have shifted water-intensive and commercial crops. (ii) It has changed the ecology by salinisation of the soil. (iii) It has increased the social gaps between the rich land owners and the landless poor.
6.explain the rice cultivation in india.
answer:It is a Kharif crop which requires high temperature, (above 25C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation. Deltas, estuaries, flood plains and valleys of rivers provide excellent conditions for the cultivation of rice
7.Explain the Wheat Cultivation in India.
answer: Wheat grows best in well-drained loams and clay loams. During germination the plant needs sufficient soil moisture. Most of the common bread wheat is grown on the alluvial soils of the Great Plains, whereas macaroni wheat is grown on the black soils of central and southern parts of India. Triticum dicoccum grows on the red soils of the Nilgiri Hills.
8. Name any four Oil Seeds Produced in India.what are their economics importance?
answer: Different oil seeds are grown covering approximately 12 per cent of the total cropped area of the country. Main oil-seeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard, coconut, sesamum (til), soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower. Most of these are edible and used as cooking mediums. However, some of these are also used as raw material in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments.
9.what is Plantation agriculture and explain four featues of it.
answer:Plantation Agriculture: It is a type of commercial farming practised in tropical and sub-tropical regions. It was introduced by the British in India.
Characteristics:i A signal crop is grown over a large area.ii It is capital intensive and done with migrant labour.iii All produce is used as raw material in industries such as tea coffee rubber sugarcane banana etc.iv Plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry both.
10.Explain the Rubber Cultivation in India,its importance
answer:Importance: Rubber is an important industrial raw material.
Geographical conditions: It is an equitable crop which is grown in tropical and subtropical areas. It requires moist and humid climate with temperature above 25°C and rainfall above 200 cm.
Two rubber-producing states: It is mainly grown in Kerala Tamil Nadu Karnataka and Garo hills of Meghalaya.
11. Difference between Rabi and Kharif crops.
answer:
12.Mohan owns a farm in Uttar Pradesh; he wishes to cultivate either Jute or Sugarcane. He shall cultivate which crop out of these two keeping in mind the conditions required for their growth? Explain.
answer:He should cultivate Sugarcane as the geographical conditions it requires are available in Uttar Pradesh. b Sugarcane grows well in hot and humid climate. c Requires a temperature of 21oC to 27oC. d Needs annual rainfall between 75 cm and 100 cm. e Irrigation is required in the regions of low rainfall. f It can be grown on a variety of soils and needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting. All these conditions are available in Uttar Pradesh.
13. describe the technological reforms taken by Indian goverment in agriculture.
answer:i Land reforms: Collectivisation consolidation of holdings cooperation and abolition of zamindari.
ii Agricultural reforms: Green revolution and White revolution.
iii Land development programmes: Provision for crop insurance against drought flood cyclone etc. establishment of Grameen banks Cooperative societies and banks for providing loans.
iv Issuing of Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme etc.
v Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV.
vi Government announces Minimum Support Price MSP and remunerative and procurement prices to clreck exploitation.
vii The government provides HYV seeds and fertilisers.
viii Government provides technical assistance and training for farmers.
ix Soil testing facilities cold storage and transportation facilities are provided by government for farmers.
14.what are the difference between commercial and subsistence farming?
answer:
15.Highlight any three differences between primitive subsistence farming and commercial farming.
answer:
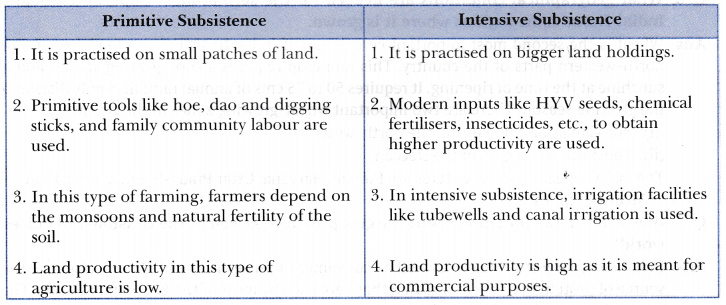
16. Highlight any three differences between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming.
answer:
17. Categorise the following as Kharif crops and Rabi crops : (i) Wheat (ii) Maize
(iii) Barley (iv) Peas (v) Bajra (vi) Tur (Arhar)
18/Categorise the following as ‘Rabi crops’ and ‘Zaid crops’ : (i) Wheat (ii)
Watermelon (iii) Fodder crops (iv) Mustard (v) Cucumber (vi) Peas
19.Categorise the following as ‘Kharif crops’ and ‘Zaid crops’ : (i) Paddy (Rice) (ii) Cucumber (iii) Bajra (iv) Cotton (v) Fodder crops (vi) Muskmelon
answer:The Kharif crops include rice, maize, sorghum, sugar cane, millet/bajra, finger millet/ragi (cereals), arhar (pulses), soyabean, paddy, groundnut (oilseeds), cotton, etc.
The rabi crops include wheat, barley, oats (cereals), chickpea/gram (pulses), linseed, mustard (oilseeds) etc.
20. Name the two major beverage crops grown in India. Describe their growing areas
answer:a) Tea : (i) An example of plantation agriculture, an important beverage crop introduced in India by the British. (ii) Grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. (iii) Require warm and moist frost-free climate, frequent showers evenly distributed over the year. (iv) A labour intensive industry, requires abundant cheap and skilled labour. (v) Major producing states are Assam, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Kerala. Apart from these, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura and also tea-producing states in the country. (vi) India is the leading producer as well as exporter of tea in the world. (b) Coffee : Importance : (i) India produces about four per cent of the world’s coffee production. (ii) The Arabica variety produced in the country is in great demand all over the world. (iii) Is cultivated in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
21,Name the two most important cereal crops grown in India. Describe the conditions required to grow these two crops.
answer:Rice and wheat are the two most important cereal crops grown in India. Rice is the staple food crop of most people in India especially in coastal regions. The geographical condition required for growth of rice are as follow :
(i) It is a kharif crop and requires hot and humid climate for cultivation. emperature above 25 degree
and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm is favourable for growth of rice.
(ii) Rich alluvial soils of the flood plains, river basins and deltaic areas which are renewed every year are ideal for rice cultivation.
(iii) Rice requires abundant rainfall or good water supply through irrigation and flooded fields during the earlier part of its growing season in June-July. Ankle deep water in the field helps the crops grow.
(iv) Plenty of cheap labour is required as most of the farming involves manual labour. (v)
Wheat is the main food crop for the people residing in the North and North-western part of the country. The geographical conditions favourable for growth of wheat are as follows:
(i) Wheat is a rabi crop and requires a cool growing season. Average temperature should be between 10 degree to 5 degree.
at the time g of sowing, but higher temperatures and bright sunshine is required at the time of harvesting for proper ripening of arrains.
(ii) Wheat requires moderate rainfall of 50 cm to 75 cm annually, evenly distributed over the growing season. A little winter rain before ripening helps in increasing the yield.
(iii) Deep alluvial clayey soils of Northern Plains and black soil of Deccan are suitable for growing wheat.
There are two important wheat-growing zones in the country : the Ganga-Satluj plains in the North-West and the black soil region of the Deccan. Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh are the major wheat growing states
22.Name any two major fibre crops grown in India. Describe the conditions required to grow these two crops.
answer:ute and cotton are the fiber crop grown in India.
Geographical condition of cotton
- Black soil is ideal for growing cotton.
- It needs warm and moist climate.
- Rainfall about 60-100 cm is needed.
Geographical condition of jute
- Loamy soil is good for growing jute.
- It need humid climate to grow jute.
- Rainfall about 160-200 cm is needed.
23.Name the two major fibre crops grown in India. Describe the conditions required for growth of these two crops with their growing areas.
answer:Cotton, jute, hemp and natural silk are the four major fibre crops grown in India.
Cotton grows well in drier parts of the black cotton soil of the Deccan plateau. It requires high temperature, light rainfall or irrigation, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine for its growth.
Jute grows well on well-drained fertile soils in the floodplains where soils are renewed every year. A high temperature is required during the time of growth.
24.Describe any five technological and institutional reforms undertaken by the Government of India to improve Indian agriculture.
answer:(i) Land reforms: Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari. (ii) Agricultural reforms: Green revolution and White revolution. (iii) Land development programmes: Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, etc., establishment of Grameen banks, Cooperative societies and banks for providing loans. (iv) Issuing of Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, etc. (v) Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV. (vi) Government announces Minimum Support Price (MSP) and remunerative and procurement prices to clreck exploitation.
25.why agricultur is called backbone of indian economy?
answer:(i) Agriculture is the mainstay of Indian economy because about 60% of our population depends directly or indirectly on agriculture.
(ii) It provides raw materials to the industries.
(iii) India earns foreign exchange by exporting agricultural products.
(iv) It contributes about 29% to the Gross Domestic Product.
(v) It provides food to over 1210.2 million population.
26.Mention geographical required for the growth of cotton in India.
answer:Temperature must be between 20 to 30 degree centigrade.
At least 210 days of frost free time.
Rainfall during and after sowing season and warm/dry conditions after flowering time.
Moderate rainfall between 50-75 cm.
Black soil / Regur soil in the Deccan trap is best suitable for cotton cultivation.
27,Mention geographical required for the growth of Tea in India.
answer:Tea is an important beverage crop.
The following are the conditions required for its cultivation.
Climate: The tea plant grows in tropical and sub-tropical regions which have deep fertile and welldrained soil rich in humus and organic matter.
Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year.
Tea bushes require frequent showers throughout the year to ensure continuous growth of tender leaves.
It needs abundant cheap and skilled labour.
Two major tea-producing states are Assam and West Bengal.
28.Name the two most important staple food crops in India. Mention the geographical conditions required for their growth.
answer: The two most important staple food crops in India are rice and wheat.
the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice are as follows. It requires high temperature—above 25°C. It requires high humidity for its growth. It requires annual rainfall above 100 cm.
The geographical conditions required for the growth of wheat arenas follows. It is a rabi crop and needs cool growing season. It requires bright sunshine at the time of ripening. It also requires 50 to 70 cm of annual rainfall, well distributed over the growing seed
29: Why is the growth rate in agriculture decelerating? How did the Government of India make efforts to modernise agriculture? Explain.
answer: The growth rate in agriculture is decelerating due to the following reasons.Reduction in public investment in agriculture especially for irrigation power rural roads etc. Subsidy on fertilisers has decreased leading to increase in the cost of production. Reduction in import of agricultural goods Lack of employment in agriculture Erratic nature of monsoon rainfallTo modernise agriculture the Government of India has taken concerted efforts like the following.Setting up of Indian Council of Agricultural Research.Setting up of agricultural universities veterinary services and animal breeding centres. Horticulture development Research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecast Improvement of rural infrastructure.
30.Jute is also known as golden fibre . expalin
answer: Jute is also known as golden fibre mainly because of its colour. It is a cash crop and can be very profitable for the economy as its export can bring in a lot of money into the economy. It is the second most important natural fibre after cotton and at present its demand has risen in India and also all around the world.











0 Comments