IMPORTANT DEFINITON OF FORESTRY
1. SOCIAL FORESTRY:Social forestry is the management and protection of forests as well as the afforestation of barren and deforested lands with the purpose of helping environmental, social and rural development.
main goal of social forestry is to grow trees and plantations to meet the growing needs of people in reference to increased demand for timber, wood, food, fuel, and food to reduce the pressure and dependency on traditional forest areas.
Effective, Efficient and Equitable (3E) criteria
Ensuring 3E outcomes is key in determining the success of a policy or program. In the context of social forestry the three components are effectiveness, efficiency and equity.
Effectiveness: outputs and benefits of social forestry
Are social forestry practices producing outcomes and benefits that contribute to poverty alleviation, empower communities and improve forest conditions
Efficiency: time and costs of social forestry
Equity: the ways benefits and costs are shared and distributed
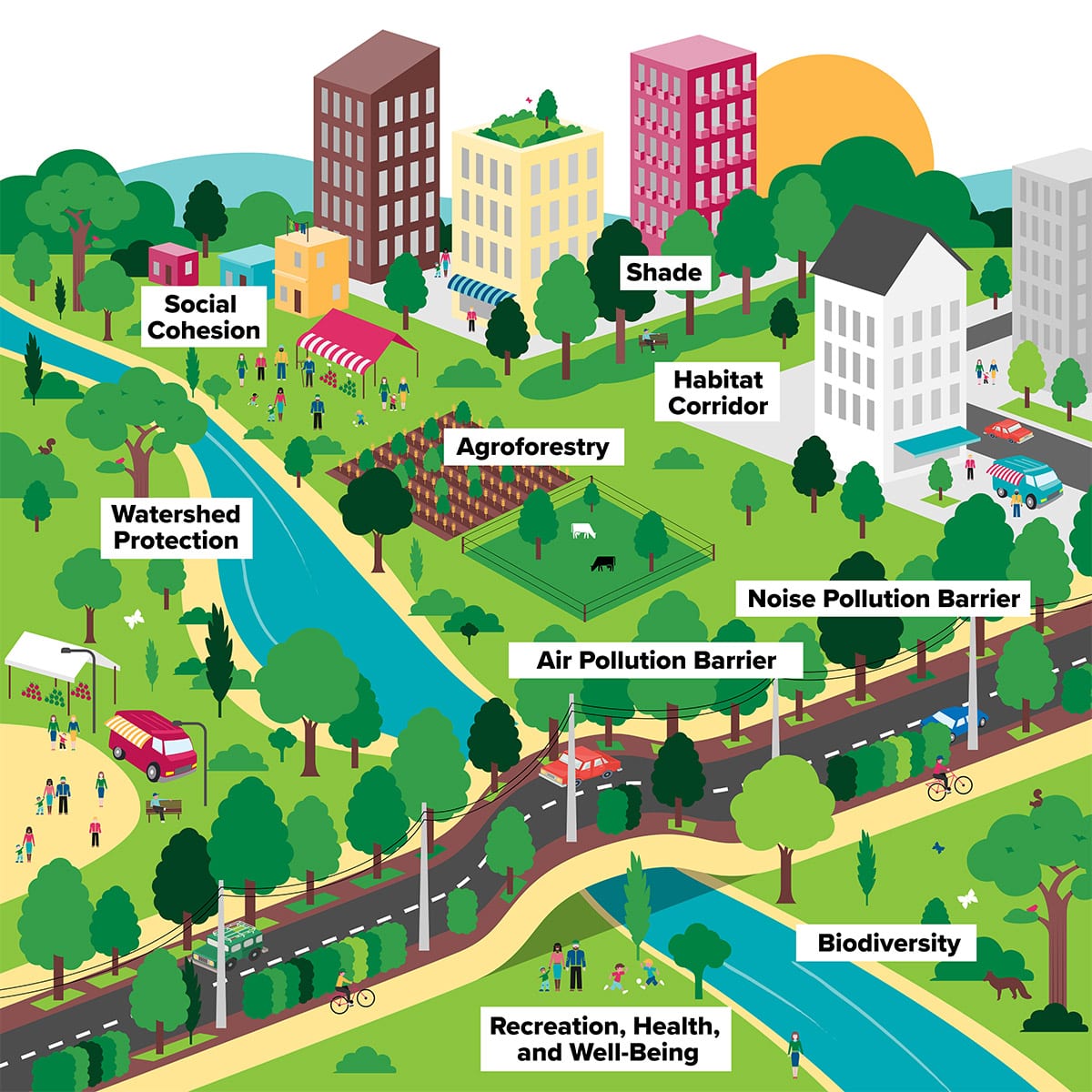
2.AGRO FORESTRY: Agroforestry is a collective name for land-use systems and technologies where woody perennials (trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc.) are deliberately used on the same land-management units as agricultural crops and/or animals, in some form of spatial arrangement or temporal sequence.
Agroforestry systems in Semiarid and arid lands Examples: Various forms of silvopastoral systems, wind breaks and shelterbelts. C) Agroforestry systems in Tropical High lands Examples: Production systems involving plantation crops such as coffee, tea, use of woody perennials in soil conservation and improved fallow.
3.COMMUNITY FORESTRY:Community forestry is a branch of forestry that deals with the communal management of forests for generating income from timber and non-timber forest products as forms of goods while in other hand regulating ecosystem, downstream settlements benefits from watershed conservation, carbon sequestration and aesthetic In the context of social forestry the three components are effectiveness, efficiency and equity.
4.COMMERCIAL FARM FORESTRY :Farm forestry is the name given to programmes which promote commercial tree growing by farmers on their own land. Farm forestry was defined by NCA (1976) as the practice of forestry in all its aspects in and the around the farms or village lands integrated with other farm operations
5. NON COMMERCIAL FORESTRY :Non-commercial farm forestry is the main thrust of most of the social forestry projects in the country today. It is not always necessary that the farmer grows trees for fuel wood, but very often they are interested in growing trees without any economic motive.
6.URBAN FORESTRY:Urban forests can be defined as networks or systems comprising all woodlands, groups of trees, and individual trees located in urban and peri-urban areas; they include, therefore, forests, street trees, trees in parks and gardens, and trees in derelict corners.












0 Comments