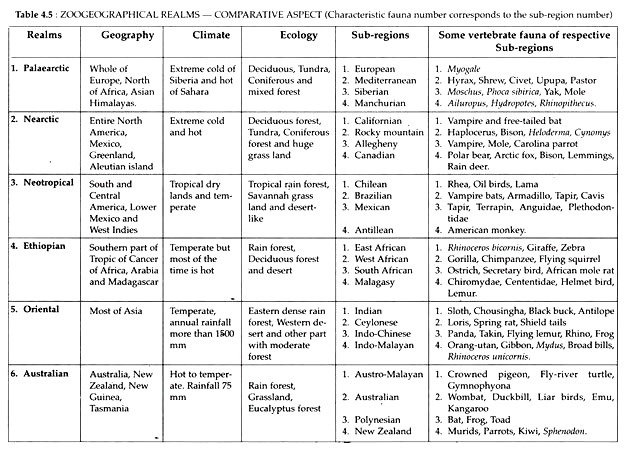
Zoo-geographical regions of the world
The distribution of living organisms on Earth is spatially structured. Early biogeographers identified the existence of multiple zoogeographical regions, characterized by faunas with homogeneous composition that are separated by biogeographical boundaries.
Although the earliest study of the geographic distribution of animals was that of Sclater in 1858 (see above History), it was Wallace who set the parameters to determine the zoogeographic regions, or realms, in his classic book, The Geographical Distribution of Animals (1876).
Alfred Russel Wallace in 1876 published a paper on zoogeographical realms. He retained the ‘six area concept’ of Sclater, but included in his study all the terrestrial vertebrates and invertebrates.
Wallace recognized three realms: Megagaea or Arcotogaea, which includes Africa, Eurasia, and North America; Notogaea, including Australia, Oceania, and New Zealand; and Neogaea, including Central and South America. His divisions, although modified, form the basis of the realms recognized today
The realms, which they described were all separated by distinctive barriers from each other. The scheme of division proposed by Wallace is presented here and the realms are separated by dotted lines on world map, which are known as Wallace’s line
Types of Zoogeographical Realms:
a. Palaearctic Realm.
b. Nearctic Realm.
c. Neo-tropical Realm.
d. Ethiopian Realm.
e. Oriental Realm.
f. Australian Realm.
Palaearctic Realm:
1.Geographically this realm consists of whole of Europe, Northern part of Africa and Asian Himalaya and Nan ling range of China.
2.Extreme cold of Siberia and extreme hot of Sahara desert are characteristic climate of this region.
3.Deciduous forest, large grass land, coniferous forest and mixed forest. Tundra area is also present in this region.
4.This faunal region includes 136 families of vertebrates, 100 genera of mammals, 174 genera of birds. Carp, Salmon, Pike, Sticklebacks are common in freshwater of this region, European Salamander, Proteius, Hynobius, Bombinator, Alytes, Didocus etc and Among 39 families of characteristic mammals, family – Seluinidae and Ailuropodie are endemic. Other mammals are porcupine, dog, wild ass, European bison, polar cat, deer, etc.are important fauna in that region
Nearctic Realm:
1.This region consists, on its north the entire of North America, in south up to Mexico, in East Greenland and in west Aleutian islands.
2.Like Palaearctic region this region also has extreme cold and hot climate.
3.Deciduous forest range, huge grass land, coniferous forest, dry land and Tundra regions are prominent ecological zonations.
4.The main animals of this region include deer, lynx, mouse, mules, wolf; bison, jack-rabbit, prairie-dog, gopher, fox; lizards, snakes, kangaroo, jerboa, hamster, hedgehog, cotton- tail, etc.
Neo-tropical Realm:
1.South and central America lower Mexico and West Indies are the constituents of this region. This region is connected with Nearctic region by central American isthmus and other parts are bordered by the sea.
2.Most parts of this region is covered by tropical dry lands. Only southern part of America experiences temperate climate.
3.In the Amazon valley there is tropical rain forest. Temperate region consists of Savannah and grassland. Western part of South America is dry and has desert like ecosystem. Argentina comprises mostly of grassland.
4.120 genus of the three families (Polycentridae, Gymnotidae and Trigonidae) are present in this region. The prominent fishes are Lepidosiren, eel, catfish, etc.Caecilia, Siphonopsis, Hyla, Salamander, frog, toad, etc and Dromicus, Boa, Epicrates, snakes, Gecko, Alligator, Chelys, etc.are important here.
Oriental Region
1.The oriental region sprawls to the south of Himalayas in South and South-East Asia.
2.Climatically this region falls in the tropical climate.
3.This faunal region represents 164 families of vertebrates, 118 genera of mammals and 340 genera of birds.
4.The main animals of this faunal region are Indian-elephants, rhino, several species of deer, antelopes, tigers, lizards, snakes, gibbons, monkeys, sun-bear, stag, tree-shrew, etc.
Ethiopian Realm:
1.It consists of southern part of the Tropic of cancer, most of the African mainland, southern part of Arabia and Madagascar.
2. Mainly temperate in most of the areas, but remains hot during most time of the year.
3.The areas on the equinoctial line and West Africa possess rain forest along the sides of large rivers. Most of the other parts are dry deciduous forest. Northern and Southern parts of the region are transformed into desert.
4.This region represents 174 families of vertebrates, 140 genera of mammals, and 294 genera of birds. The main animals of this region include springbok, jerboa, zebra, gnu, giraffe, elephant, ostrich, lions, cheetah, gorilla, chimpanzee, monkey, forest elephants, etc.
Australian Realm:
1.Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, Tasmania and some islands of adjacent areas are included in this realm..
2.Hot and temperate, both types of climate are present here. Average rainfall in a year is 75 mm.
3.Rain forest, grassland, eucalyptus forest are prominent ecological characters.
4. There are 141 families of vertebrates.
5.Neoceratodus Lung fish, Osteoglocidos, Gadopcidae, etc.,Xenorhinidae family is present in New Guinea only.,Pseudophryne, Pachybatrachus, Helioporus, Pelodyrus are other important members. Total 11 families are recorded.Important snake families are Phithonidae and Elapidae: Pizopidae, Apracidae, Liadidae are prominent lizards. Sphenodon of Rhynchocephalidae family is the famous relict of reptiles present in New Zealand.Ornithorhynchus (a marsupial), Tachyglossus (ant eater), Kangaroo, Dasyures, Dendrolagus (climbing kangaroo), Petaurus (flying opossum), wolf are the remarkable members.









0 Comments