ISC CLASS 12 CHAPTER 3
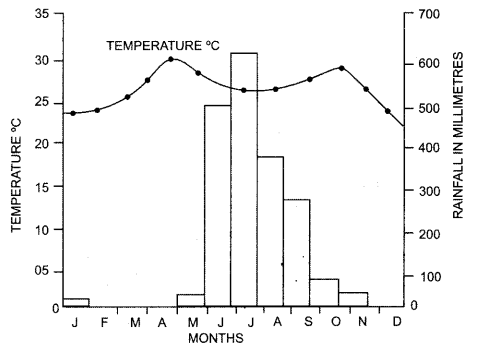
1. Study the temperature
and rainfall graph of station X given below and answer the questions that
follow
(i) Is the
location of station X inland or coastal ?
(ii) What is the cause
of sudden fall of temperature in July, even though it is a summer month ?
(iii) Mention one main
feature of the climate experienced by the station X
Answer: (i) Inland.
(ii) The cause of sudden fall of
temperature in July is due to the onset of the monsoon season. There is a fall
of temperature from July to September because of rainfall during this period.
(iii) The station experiences
continental type of climate with marked seasonal changes with respect to
temperature and rainfall.
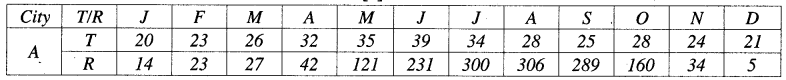
2. Study the climatic data provided in the table below for a city A
in India and answer the questions that follow
T = Mean monthly
temperature in degree Celsius (°C).
R = Average monthly
rainfall in millimetres (mm).
(i) What is the cause of
low rainfall in station A ?
(ii) Calculate the range
of temperature of this station.
Answer: (i) Rain shadow region.
(ii) (18°C) – (-8°C) = 26°C.
3. Study the climatic
data provided in the table below for a city A in India and answer the questions
that follow : [2]
(i) define: Southern Oscillation
Answer: The Southern oscillation
is a pattern of meteorological changes which are often observed between Indian
and Pacific oceans. Whenever the surface level pressure is high over the
Pacific Ocean and low over Indian Ocean, the south west monsoons in India tend
to be stronger. If the surface level pressure is high over Indian Ocean and
high over Pacific Ocean, the southwest monsoon is likely to be weaker.
(ii) Northern Mountain Ranges
Answer: The Himalayas and the
adjoining mountain ranges protects India from the bitter cold dry winds of
Central Asia during winters. The mountains also act as an effective physical
barrier for the rain bearing southwest monsoons to cross the northern frontiers
of India.
T = Mean monthly temperature in
degree Celsius (°C).
R = Average monthly
rainfall in millimeters (mm).
(i) Mention two main
features of the climate experienced by station A.
(ii) Calculate the
annual rainfall for station A.
Answer: Two main features of the
climate experienced by station A :
(i) 1. The range of temperature is
as high as (39°C – 20°C) = 19°C.
2. The station receives rain from
south west monsoon.
(ii) 1552 mm
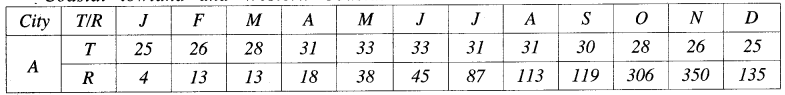
4. Study the climatic data
provided in the table below for a city A in India and answer the questions that
follow :
T = Mean monthly temperature in
degree Celsius (°C).
R = Average monthly
rainfall in millimetres (mm).
(i) Account for the
maximum rainfall in the months of October-November.
(ii) Account for the low
rainfall in city A during the months of June to September.
Answer: (i) Retreating Monsoon and
Northeast Monsoon.
(ii) As the city is located in the
eastern coast it receives very low rainfall from the Bay of Bengal Branch of
Southwest Monsoon as it runs parallel to the coast.
5. Briefly discuss the
role of El Nino in Indian climate.
Answer: El Nino is a narrow warm
current which sometimes appear off the Coast of Peru in South America during
December. It increases the surface water temperature of the sea by 10°C. This
warming of Tropical Pacific water affects the global pattern of pressure and
wind system including the Monsoon winds in the Indian Ocean causing severe
drought and flood.
6. Study the climatic
graph of station A given below and answer the questions that follow
(i) Give a reason as to
why extreme low temperature is indicated for station A.
(ii) Name the month when
the highest amount of rainfall is received.
Answer: (i) Station A is at a high
altitude and is surrounded by lofty mountains. It is out of influence of the
monsoon.
(ii) The months of July and August
receive the highest rainfall.
7. Study the Temperature-Rainfall graph of station X below and
answer the questions that follow
(a) Is the location of
station X Inland or coastal ? Give a reason for your answer.
(b) Which branch of the
South West Monsoon brings, rain from the month of June to September ?
Answer: (a) Yes, it is Coastal:
The annual range of temperature is only 6°C. The area is influe- need by the
moderating influence of the sea.
(b) The Arabian sea branch of
south-west monsoon.
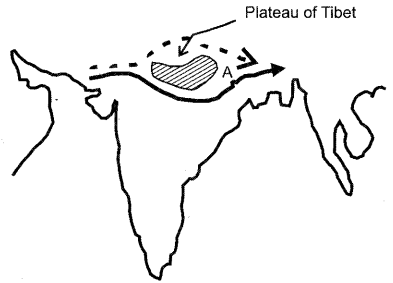
8. In the diagram given
below, A represents the path of an upper atmospheric air movement in the cold
weather season.
(a) Name A
(b) Explain how A
influences the weather of India during winter season.
Answer: A is the Westerly Jet
stream.
(b) During the winter season in
India, this jet stream has a great influence on the weather of India as it
attracts the western disturbances, which originate in Mediterranean Sea and
give a light rain in winter. Hail storm in the north-western plains and occasional
heavy snowfall in the hilly regions also takes place.
9. State any two ways in
which Himalayas affect the Indian climate.
Answer: 1. Himalayas prevent the
cold winds of Central Asia from entering India. This prevents India from
experiencing very cold winters.
2. The Himalayas also prevent the
rain-bearing monsoon winds from leaving the country thus allowing the country
to receive sufficient rainfall.
10. Mention two reasons
for the ‘break’ in monsoons.
Answer: 1. Failure of the tropical
depression.
2. Dislocation of the monsoon
trough (ITCZ) over North India
11. What is the El Nino?
Answer: El Nino is a narrow warm
current which sometimes appears off the coast of Peru in South America during
December. It is a temporary replacement of the cold Peru current which normally
flows along this coast.
12.How does it affect
the climate of India ?
Answer: This warm current can
increase the surface water temperature of the sea by 10°C. Warming of tropical
pacific waters affects the global pattern of pressure and wind system including
the monsoon winds in the Indian Ocean.











0 Comments