RIVER: EROSIONAL LANDFORMS
1.erosion work
2. transportation work
3. deposition work
1) Erosion is the most important of the three types of river functions (namely , erosion , carrying and sedimentation) . Because the rest of the river depends on erosion and the other two works directly and indirectly. The river continues to flow at different levels and in different ways due to its special properties such as strong kinetic energy, water pressure, solution etc. This type of work is called Erosional Works of River .
Characteristics : Erosion of the river - Its characteristics are as follows -
a) The amount of erosion of the river depends on the speed of the river, the amount of water, the structural nature of the local rock layer, etc.
B)The erosion of the river largely controls the other two functions of the river, namely, the carrying and the sedimentation.
C) As a result of erosion of the river, the overall height and width of the area concerned decreases.
D) The river basin changes.
Process : River erosion - There are basically five types of process. Namely -
1. Hydraulic action: The relatively soft and loose boulders along the river bank and along the river are eroded and broken by the rapid flow of the river and carried forward by the water flow . This is called hydraulic action of the river .
2. Attrition: Boulders collide with each other to break up into relatively small boulders and eventually into sand. This is called attrition of the river .
3. Corrosion : Rivers carrying rocks collide with river basins as they move. As a result, the riverbed is severely eroded. Such erosion of a river is called corrosion .
4. Solution : Due to the special nature of the local rock layer (eg limestone, salt rock, etc.) or the special nature of the river water (eg, excessive acidity or alkalinity), the rock in the course of the river often melts or dissolves rapidly. Such erosion of the river is caused by soluble erosion(Solution) says.
Landforms created by the erosion of the river - The landforms created as a result are -
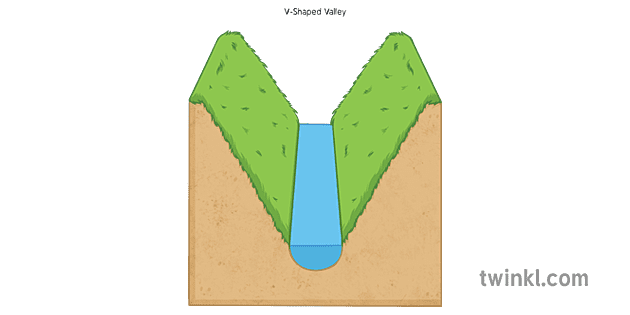
1. 'V' - shaped valleys and gorges:
V' - Shaped River Valleys (Definition):
Definition : In riverine streams, the river bed and river bed collide with boulders carried by the strong currents of the river, causing rapid erosion of the river bed. As a result, the river valleys gradually take on the shape of the English letter 'V'. It is called 'V' - shaped river valleys .
For example, in the Himalayas of Shatadru , Indus, Teesta and other rivers, such 'V'-shaped river valleys have formed in the hilly path.
Characteristics: The features of 'V' shaped river valley are as under -
A) This type of river valley is usually seen in upstream or hilly streams.
B) The slopes on both sides of this valley are formed as a result of the combination of river and meteorology.
C) The slope of the valley is very steep in areas formed by hard rock and it is less sloping due to rapid erosion of rock in soft rock formed areas.
D) The 'I'-shaped river valleys are often eroded by erosion, rainfall erosion or meteorological erosion and over time it takes the form of 'V'-shaped valleys.
Gorges: Definition: '
V' -shaped river valleys are called gorges when they are very deep and the banks are very steep .
For example: Peru's Kalka River Gorge (about 4,085 m), Nepal's Kaligandaki River Gorge (more than 5,000 m in part), China's Ichang River Gorge, Shatdru River Gorge (about 5,000 m when entering India from Tibet), Alpine River
Characteristics: The features of the gorge are as follows -
a) The gorge is formed mainly in the upper reaches of the river or in the hills.
B) The gorge is very deep and narrow in nature.
C) The walls on both sides of the gorge are rocky and steep in nature.
D) Mainly formed in humid aquifers.
E) 'V'-shaped river valleys gradually become deeper and steeper and become gorge.
F)Gorge is formed when the erosion of the slopes on both sides of the river valley due to meteorology cannot keep pace with the rapid erosion of the river.
G) If a region rises again as a result of an earthquake, then the river rejuvenates in that region and erodes its main valley more deeply and forms deep canyons. Many of the world's gorges are formed as a result of rapid erosion of rivers in harmony with the lands thus raised [e.g., Indus and Brahmaputra river gorges
Canyons:
meaning: Canyon is a Spanish word meaning pipe . Definition : In arid dry desert hilly areas or plateaus, the erosion is almost completely stopped due to lack of water in the river, but when the erosion makes the steep English 'I'-shaped valley deeper, steeper and narrower, it is called canyons .
For example , the Colorado River in the USA The Grand Canyon is the longest canyon in the world, about 482 km long and in places more than 2000 meters deep.
Characteristics : The features of Canyon are as follows -
a) It is mainly found in arid regions.
B) The sides are very steep and narrow in nature.
C) The river bed is at the very bottom of the valley.
D) Excess of soft rock plays a special role in canyon formation.
2. 'I' - shaped valley('I' - shaped Valleys)
rainless arid desert highlands or plateaus, the erosion is almost completely stopped due to lack of water in the river, but continuous erosion results in continuous 'I' - shaped narrow river valleys. This is called 'I' - shaped river valleys . For example, 'I' shaped river valleys can be seen in some places along the Indus in the Himalayas
Characteristics : The features of 'I'-shaped river valley are as follows -
A) The side of 'I'-shaped river valley is very steep in nature.
B)Mainly seen in areas where adequate water supply is low.
C)The excess of soft rock layers plays a special role in the formation of 'I' shaped river valleys.
D) It is mainly caused by the effect of non-lateral degeneration.
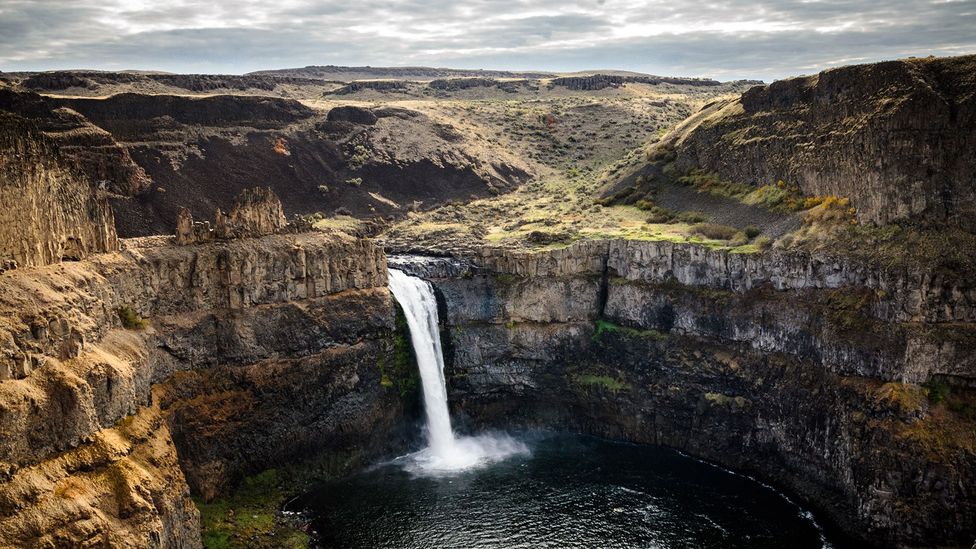
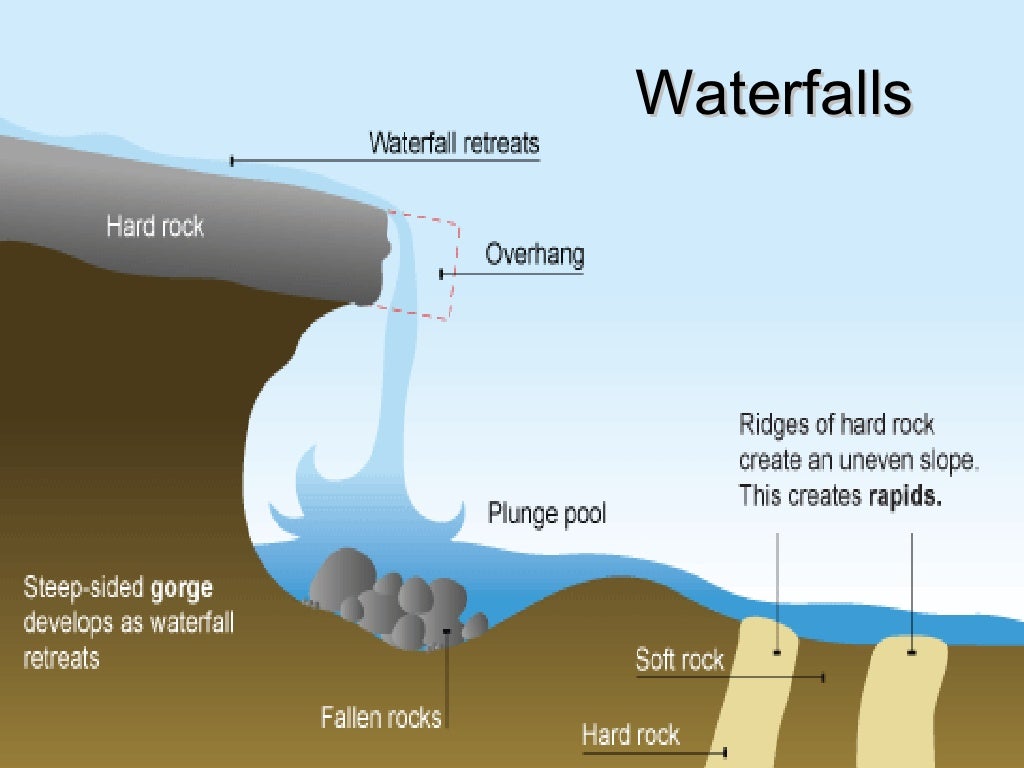
3. Waterfalls
When hard rock and soft rock are placed horizontally in the course of a river in a hilly course, the strong currents of the river cause the soft rock to erode faster than the hard rock and form a steep slope. As a result , the river continues to flow down the steep slope. These are called waterfalls .
For example , India has 2 of the 36 major waterfalls in the world . These two waterfalls are Jersoppa Falls or Yoga Falls (about 253 m) formed on the Sarabati River and Shivsamudram Falls on the Kaveri River. Also notable among the other major waterfalls in the world are the Angel Falls (about 989 m) on the Rio Caroni River in Venezuela, South America which is the highest waterfall in the world, Niagara Falls on the St. Lawrence River in Canada, Victoria Falls on the Zambezi River in Africa.
Structure: Waterfalls are basically formed by following the following special processes. Namely -
a) When hard and soft rocks are placed horizontally in the course of the river in high flow or hilly flow, as a result of low erosion of the river, the soft rock tends to erode faster and more than the hard rock . The result is a steep slope, the river jumps up and down, creating a waterfall.
B) If hard rock is placed horizontally in the course of the river, then that hard rock is less eroded than the surrounding soft rock. As a result, it rises and small waterfalls are formed. Again, if these hard rocks are located parallel to the soft rock then the waterfall forms vertically.
E.g.- Niagara Falls, formed on the St. Lawrence River, with the corresponding rock layer composed of hard rock dolomite and the lower part composed of soft rock shale and sandstone.
C) Often the edge of the plateau suddenly descends steeply. As a result, many small waterfalls are formed on the edge of those plateaus.
For example - Hundru Falls created in Subarnarekha river
d) If there is any gap in the course of the river then the river jumps from the upper part of the fault to the lower part and waterfall is formed. In this case, if there is hard rock in the upper part of the fault and soft rock in the lower part, then this type of waterfall is long lasting.
E.g. Victoria Falls on the Zambezi River in Africa
e) Major glaciers formed as a result of glacier erosionHanging valleys are formed much deeper than the other small glacier valleys surrounding the valley . Flowers are formed when the river flows later in this hanging valley area.
Classification : There are three types of waterfalls according to their nature and characteristics. Namely -
a) Rapid : When the slope of a waterfall is low, it descends step by step from above. This is called rapid current or rapid .
For example, in the Zaire River, 11 such rapid currents or rapids have been created to form the Livingstone Falls. Also, rapids are seen in the Chhotanagpur Plateau.
B) Cascade : When a rapid waterfall becomes smaller and flows into a smaller waterfall, it is called a cascade .
E.g.Jonha Falls in Ranchi, Tears of the Glenn Falls in Northern Ireland, etc.
and
c) Cataract : A cataract is a volcanic waterfall when it jumps far below the top of the slope in a huge body of water . For example, Victoria Falls on the Zaire River in Africa
4. Truncated Spur
Definition : In the hilly areas, the river continues to erode at a high rate of erosion. At this point, the river erodes the protrusions of the ridges in its course and moves somewhat straight. The projections of such eroded rock veins are called truncated spurs . For example, in the highlands of the Himalayas, the Teesta, Torsa, Mahananda, Jaldhaka, etc., many such cut-off cliffs can be seen
Characteristics : The characteristics of the cut ridges are as follows -
a) They are mainly found in the highlands in the high reaches of the fast flowing river.
B) These are erosive landforms of the river
5. Interlocking Spur:
Definition : In the hilly areas, when hard rocks are blocked in the course of the river, the river starts to bend. As a result, one side of the river hides the other. As a result, the course of the river is not directly visible from a great distance, and from a distance it appears that the ridges are bound or chained, which is why they are called interlocking spurs .
For example, in the Himalayas, in the course of the river Mandakini , there are numerous such bounded ridges or chained ridges.
Characteristics : Characteristics of bounded ridges or chained ridges are as follows -
a) They are mainly found in the highlands of the river.
B) These are erosive landforms of the river.
C) These are riversHides the visibility of the stream from a distance.
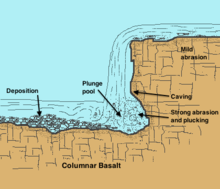
7. Plunge pools:
Definition : When a river falls down from a high part of the slope in its course, the impact of water currents and carried rocks creates almost round holes in the river bed. These are called plunge pools.
For example, such a waterfall can be seen at the fall of Hundru Falls in the Golden Line.
Characteristics : The features of waterfall wells are as follows -
a) They are almost round in shape.
B) These can be deep enough.
C) They become visible when the amount of water in the river decreases during the dry season.
D) Their shape and depth depends on the nature of the river, the difference in slope, the amount and nature of rocks carried.
8.Pot Holes:
Definition : In the process of friction, the rocks carried along the current of the river form small, almost round holes in the river bed. These are called pot holes. For example, there are numerous mouth wells in the river basins of the rivers flowing in the hilly areas of the himalaya
Characteristics : The characteristics of POTHOLE are as follows -
a)It is mainly formed in the hilly areas in the high flow of fast flowing river.
B) They deepen the river bed.
D) They are mainly formed in the process of river erosion.
E)The shape and number of mouth wells depend on the velocity of the river flow, the shape and amount of rock carried, the nature of the rock forming the river bed, etc.
F) Mouth wells are usually very round or almost round in appearance.
CONTINUE............
















0 Comments