Difference between El Nino and La Nina// ENGLISH NOTE
|
TOPIC |
El Nino |
La Nina |
|
MEANING |
Derived from the Spanish term which represents
“little boy” |
Derived its name from the Spanish term which represents
‘little girl’. |
|
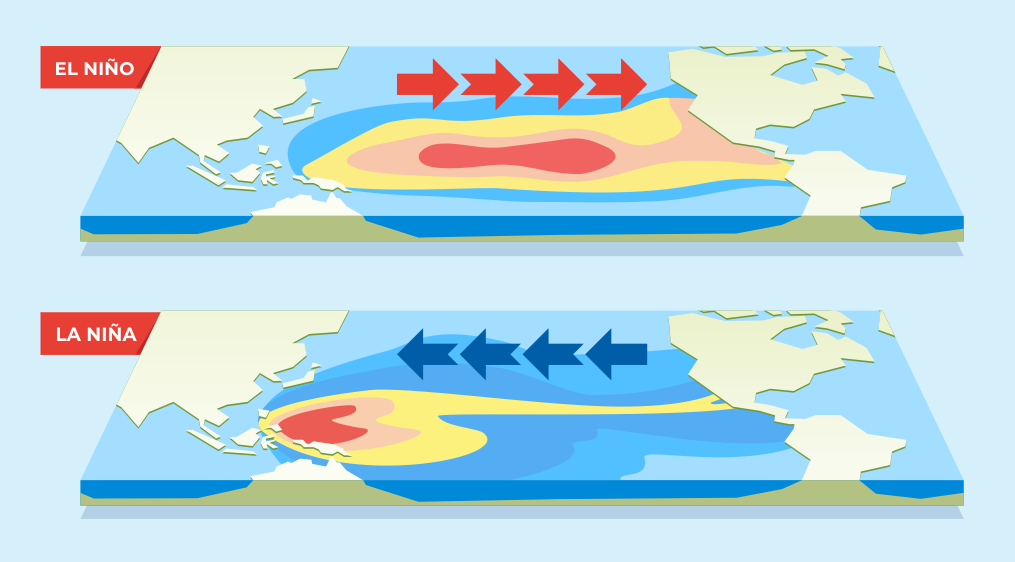
TEMPERATURE AT SEA
SURFACE |
It
is warmer than normal sea-surface temperatures. It is a warming of the
Pacific Ocean between South America and the International Date Line, centred
directly on the Equator, and moves towards several degrees of latitude to
either side of the equator. |
It
is cooler than normal sea-surface temperatures. It originated when cooler
than usual ocean temperatures occur on the equator between South America and
the International Date Line. |
|
PRESSURE |
It is laden with high air surface pressure in the western
Pacific. |
It contain low air surface pressure in the eastern Pacific |
|
TRADE WINDS |
It
originated when tropical Pacific Ocean trade winds die out and ocean
temperatures become unusually warm. |
It
occurs when the trade winds blow unusually hard and the sea temperature
become colder than normal. |
|
CORIOLIS FORCE |
It decreases in the strength of the Coriolis
force. |
It increases in the strength of the Coriolis force. |
|
SEASONS |
It
has great impact on season pattern because it makes warmer and drier than
average in the Northwest of pacific during winters and wetter in Southwest of
pacific and experience reduced snowfalls. |
Winters
are wetter and cause above-average precipitation across the Northwest of
pacific and drier and below average precipitation in South west of pacific. |
|
CYCLONES |
Wind speed is low. |
It had a greater tendency to trigger intense tropical
cyclones as wind direction changes pilling up water between Indonesia and
nearby areas as winds from Africa onwards gets blocked. |
|
OCEAN WATERS IN
PACIFIC |
Warm
water approaches the coasts of South America which results in reduced
upwelling of nutrient-rich deep water impacting impacts on the fish
populations. |
Cold
water causes increased upwelling of deep cold ocean waters numbers of drought
occurrence, with more nutrient-filled eastern Pacific waters. |
|
EFFECTS |
Heavy rains in Ecuador and Peru; Heavy rains in southern
Brazil but drought in north East Brazil; Drought in Zimbabwe, Mozambique,
South Africa, Ethiopia; Warm winter in the northern half of the United States
and southern Canada. Drought, Scant rains off Asia including India,
Indonesia, and Philippines; Coral bleaching worldwide; Drought in eastern
Australia |
Causes drought in Ecuador and Peru. Created low
temperature, high Pressure in Eastern Pacific. Heavy floods in Australia;
High Temperature in Western Pacific, Indian Ocean, Off coast Somalia and good
rains in India. |








0 Comments