ICSE
CLASS 10 GEOGRAPHY – SOIL // IMPORTANT QUESTIONS PART 1
Question
1: What is the soil?
Answer: Soil
is important natural resource .‘Soil’ means the uppermost layer of the earth’s
crust, which contains the organic as well as minerals which all life depends on
it.
Question
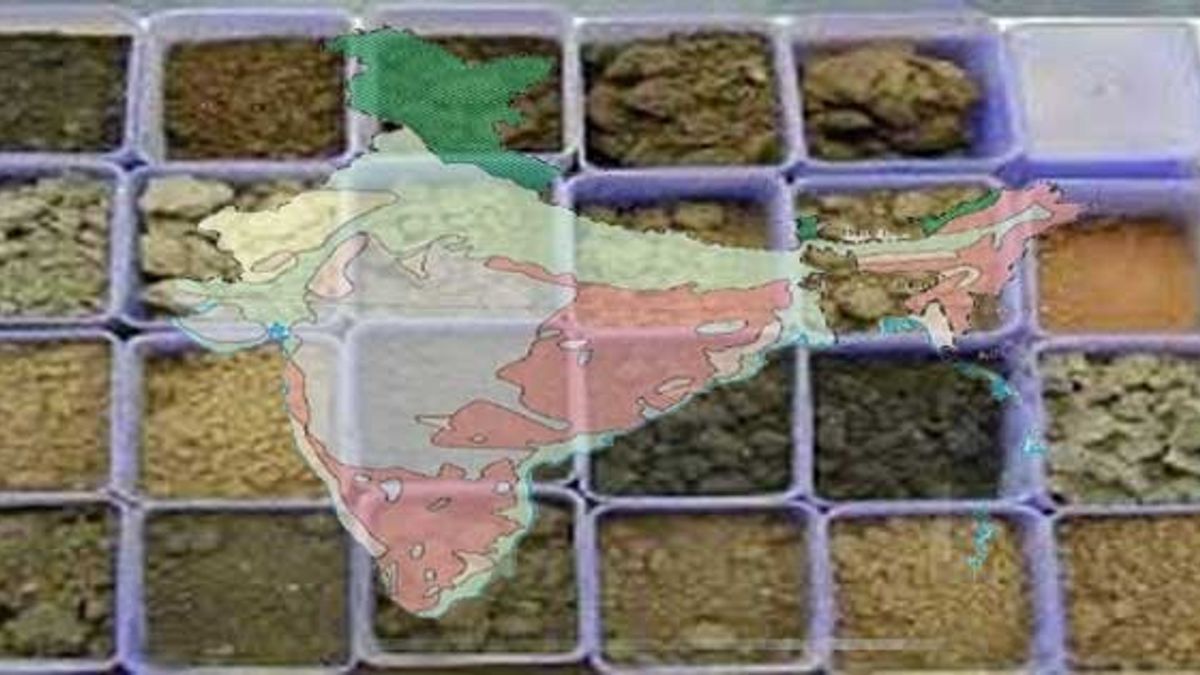
2: Name the four types of soil.
The four types
of soil are-
1. Alluvial soil
2. Black soil
3. Red soil
4. Laterite soil
Question:3
State any two factors responsible for the formation of soil.
Answer: Two
factors responsible for the formation of soil are-
1. Parent material
2. Weathering of rocks.
Question
4: Name one important constituent of soil that adds fertility to the soil.
Answer: One
important constituent of soil that adds fertility to the soil is humus.
Question
5: Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
The colour of alluvium soil varies in different areas.
(ii)
Khadar is more fertile than bhangar soil.
(iii)
Black soil has a kind of self-ploughing characteristic.
Answer
(i) The colour
of alluvium soil varies in different areas because its shades depend on the
depth of deposition, the texture of the materials and the time taken for
maturity.
(ii) Khadar is
more fertile than bhangar soil as khadar
is new layers that are deposited year after year during monsoon floods.
(iii)
Black soil has a kind of self-ploughing characteristic
because during dry season, it shrinks and develops big cracks which help in air
circulation. This characteristic causes a kind of self-ploughing.
Question
6: How are alluvial soils formed?
Answer: Alluvial
soil is formed by the sediments brought down by rivers. The rivers deposit very
fine particles of soil called alluvium in their plains during the course of
their long journey. The resultant alluvial soil is known as riverine soil.
Question
7 Mention any two advantages of alluvial soil.
Answer:Two
advantages of alluvial soil are-
1. It is light and porous. So, it is easily
tillable.
2. It is suitable for the growth of a large
variety of rabi and kharif crops.
Question
8 (i) Why is soil a valuable resource for India?
Answer: Soil
is a valuable resource for India because agriculture is the main occupation in
India. Soil supports agriculture and it is the source of nutrients for many
forms of life.
(ii)
Why is black soil considered a productive soil?
Answer: Black
soil is considered a productive soil because it has high moisture retention
capacity and more clay content which responds well to irrigation. It is
suitable for the cultivation of cotton, jowar, wheat, linseed, gram, citrus
fruits and vegetables, tobacco and sugarcane.
Question
9 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Different regions in India have different kinds of soil for
agriculture.
Different
regions in India have different kinds of soil for agriculture because India is
a vast region with varied natural environment. Several physiographic regions
and different types of climate lead to the formation of different types of soil
in different regions.
(ii)
Alluvial soils vary in texture.
Alluvial
soils vary in texture as in the upper reaches of the river valleys, the soil is
dry, coarse, porous and sandy. Soil particles are large and non-uniform but as
we move further down a river valley, the soil particles become smaller and more
uniform. They are more compact, less compact and more moist.
(iii)
Nearly all types of crops grow well in riverine soils.
Nearly all
types of crops grow well in riverine soils because alluvial soil is a mixture
of sand, clay and silt. It is rich in mineral and easily tillable. Its
composition makes it suitable for the growth of a variety of crops.
Question
10: Give two characteristic features of the soil found most suitable for
growing cotton and sugarcane in Maharashtra.
Answer: Black
soil is suitable for growing cotton and sugarcane in Maharashtra. Its
characteristics are-
1. It is black in colour.
2. It has high quantities of lime, iron,
magnesium and generally poor percentage of phosphorus, nitrogen and organic
matter.
Question
11: Name one soil of volcanic origin commonly found in India. Name one crop
widely grown on this soil.
Answer: One
soil of volcanic origin commonly found in India is black soil. Cotton is widely
grown on this soil.
Question
12:(i) Name the process by which Laterite soil is formed.
(ii)
Mention one disadvantage of Laterite soil.
Answer
(i) Laterite
soil is formed as a result of atmospheric weathering of rocks under the
conditions of high rainfall and temperature with alternate wet and dry periods.
It is the residual soil formed by leaching due to tropical rains.
(ii) One
disadvantage of Laterite soil is that it does not retain moisture and hence, is
infertile.
Question
13 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Deltaic alluvium is more fertile than the coastal alluvium.
(ii)
Black soil is largely found in the Deccan Trap region.
(iii)
Black soil is often referred to as Cotton soil or Regur soil.
Answer
(i) Deltaic
alluvium is more fertile than coastal alluvium as new layers are deposited year
after year during monsoonal floods. Also, deltaic alluvium is composed of fine
silt and clay whereas coastal alluvium is full of lime nodules.
(ii) Black
soil is found in the Deccan trap region because this region is formed due to
the deposition of lava produced by the volcanic eruption. When lava rocks
breaks down into finer particles due to weathering, it results in the formation
of the black soil.
(iii) Black
soil is often referred to as Cotton soil or Regur soil because it is black in
colour and is suitable for cotton cultivation.
Question
14 State the two sub-categories into which alluvial soil is generally divided.
Which one of them is superior to the other? Why?
Answer
Two
sub-categories into which alluvial soil is generally divided are khadar and
bhangar.
Khadar is
superior to bhangar because it is more fertile as new layers are deposited year
after year during monsoon floods.
Question
15 What are the characteristics of alluvial soil?
Answer
The
characteristics of alluvial soil are:
1. Colour — The colour of alluvial soil varies
from light grey to deep black.
2. Texture — In the upper reaches of the
valleys, the soil is dry, coarse, porous and sandy with large and non-unifrom
soil particles. In the lower reaches of the river valley, the soil particles
become smaller and more uniform and more moist.
3. Minerals — It varies in nature from sandy
loam to clay. It is fertile with minerals like iron, magnesia, alumina, potash
and lime but poor in phosphorus, nitrogen and organic matter.
Question
16 (i) Which soil is suitable for growing coffee in Karnataka?
(ii)
Mention two main characteristics of this soil.
Answer
(i) Laterite
soil is suitable for growing coffee in Karnataka.
(ii) Two main
characteristics of this soil are-
1. It is red in colour due to the presence of
iron oxide.
2. It is of a coarse texture, soft and friable.
Question
17 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Laterite soil is useful for construction purpose.
(ii)
Soils of the Western Ghats are affected by wind erosion.
(iii)
The foothills of the Himalayas are prone to excessive soil erosion.
Answer
(i) Laterite
soils are used as a building material because they become hard like iron when
exposed to air. So, they are used as a building material. Laterite soils are
red in color due to the presence of iron oxide. These soils are generally coarse
in texture and friable and porous in nature.
(ii) Soils of
the Western Ghats are affected by wind erosion because a large chunk of Western
zone is arid or semi-arid and wind erosion is a result of extreme form of soil
degradation due to aridity.
(iii) The
foothills of the Himalayas are prone to excessive soil erosion because the
vegetation over there is very less. There are not many plant or tree roots to
hold the soil in place, which makes the foothills of the Himalayas prone to
excessive soil erosion.
Question
18 Name two States in India where Regur soil is found.
Answer
Regur soil is
found in Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
Question
19 Give two points of difference between Regur and Alluvial soil.
Answer
|
Regur soil |
Alluvial soil |
|
It is formed by the weathering of lava
rocks |
It is formed by deposition of sediments
by rivers. |
|
It is of black colour. |
Its colour varies from light grey to deep
black. |
Question
20(i) Besides cotton, name the crops which grow well in Regur soil.
(ii)
In what way does Regur soil help agriculture?
Answer
(i) Besides
cotton, jowar, wheat, linseed, gram, citrus fruits and vegetables, tobacco and
sugarcane grow well in Regur soil.
(ii) Regur
soil helps agriculture as it is very fertile. In any season, it has moisture
stored in its subsoil. This allows dry farming as well. In dry season, it forms
big cracks which help in air circulation, and causes a kind of self ploughing.
Question
21 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Jowar is grown in Maharashtra.
(ii)
Bajra is grown in Rajasthan.
(iii)
Sugarcane is grown in Uttar Pradesh.
Answer
(i) Jowar is
grown in Maharashtra because of the black regur soil which is rich in lime,
potash-magnesium, carbonates, allumina and calcium.
(ii) Bajra is
grown in Rajasthan because of the sandy soil found in this region. It is rich
in soluble salts.
(iii)
Sugarcane is grown in Uttar Pradesh because the climatic conditions and
presence of alluvial soil support the cultivation of sugarcane.
Question
22 Name two states where red soil is found. Mention two important crops grown
in this soil.
Answer
Two states
where red soil is found are Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Two important crops grown
in this soil are rice and tobacco.
Question
23 State two advantages of this type of soil.
Answer
Two advantages
of this type of soil are-
1. It is porous, loose and aerated.
2. It is ideal for dry farming.
Question
24 (i) How is red soil formed?
(ii)
How is this soil suitable for dry farming?
Answer
(i) Red soil
develops on old crystalline rocks. Under prolonged weathering by rainfall,
ancient crystalline and metamorphic rocks of the peninsular plateau break up to
form this soil.
(ii) This soil
suitable for dry farming as it is formed in areas with poor rainfall.
Question
25 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Black soil is also called lava soil.
(ii)
Red soil is red in colour and its colour varies from yellow to brown.
(iii)
Jute is cultivated in West Bengal.
Answer
(i) Black soil
is also called lava soil because it is formed by the denudation of volcanic
rocks.
(ii) Red soil
is red in colour as it contains large amounts f iron oxide. At several places,
its colour changes and it appears brown or grey. It looks yellow when it occurs
in a hydrated form.
(iii) Jute is
cultivated in West Bengal because the alluvial soil found in West Bengal is
very fertile and supports jute cultivation.
Question
26 What is soil erosion? Name the areas of soil erosion in India-
(i)
for wind erosion
(ii)
for running water erosion
Answer The
removal of the top soil cover by water, wind and human activities is called
soil erosion.
(i) Wind
erosion affects the dry areas of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Haryana
(ii) Running
water erosion affects the badlands of Chambal and Yamuna river, the piedmont
zone of western Himalayas, the Chotanagpur plateau, the Tapi-Sabarmati valley
and the regur soil area of Maharashtra.
Question
27Give two methods used to prevent soil erosion.
Answer
Two methods
used to prevent soil erosion are-
1. Terrace farming
2. Shelter belts
Question
28(i) What is meant by soil conservation?
(ii)
State two measures to conserve soil in hilly areas.
Answer
(i) Soil
conservation means prevention of soil loss from erosion or prevention of
reduced fertility of soil caused by over-use, acidification, salinisation or
other types of soil contamination.
(ii) Two
measures to conserve soil in hilly areas are-
1. Terrace
farming- Terraces act as bunds and prevent soil erosion by running water.
2. Contour
Ploughing- Ploughing along contours on a slope prevents soil erosion by running
water.
Question
29 Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i)
Shelter belts reduce soil erosion in arid areas.
(ii)
Rural development will influence soil conservation.
(iii)
Water harvesting aids in soil conservation.
Answer
(i) Shelter
belts reduce soil erosion in arid areas because planting trees in several rows
checks wind erosion.
(ii) Rural
development will influence soil conservation as in the programmes of rural
development, villagers are provided with the techniques of how to improve
vegetative cover and the steps required to be taken for preventing soil
erosion. The farmers are briefed about the farming methods (such as strip
cropping and shelter belts) to be followed to reduce soil erosion.
(iii) Water
harvesting aids in soil conservation as it reduces soil erosion and flood
hazards by collecting rainwater and reducing the flow of water which causes the
removal of fertile top soil.
Question
30 How does deforestation lead to soil erosion?
Answer
Deforestation
exposes the soil to water and wind, which leads to soil erosion.
Question
31 State two methods of controlling erosion of soil caused by running water.
Answer
Two methods of
controlling erosion of soil caused by running water are construction of dams
and plugging gullies.
Question
32 Name two important agents of erosion. For each, state one method of
controlling the erosion caused.
Answer
Two important
agents of erosion are water and wind. Water erosion can be controlled by the
construction of dams. Wind erosion can be controlled by making shelter belts.
Question
33 Explain briefly the need for conservation of soil as a natural resource.
Answer
There is an
acute need for conservation of soil as a natural resource because of its
adverse effects which include the following-
1. Loss of fertile topsoil with its mineral
content
2. Lowering of the water table
3. Drying of vegetation and extension of arid lands
leading to an increase in the frequency of drought and floods
4. Silting of river and canal beds
5. Recurrence of landslides
6. Adverse effect on economic prosperity and
cultural development











0 Comments